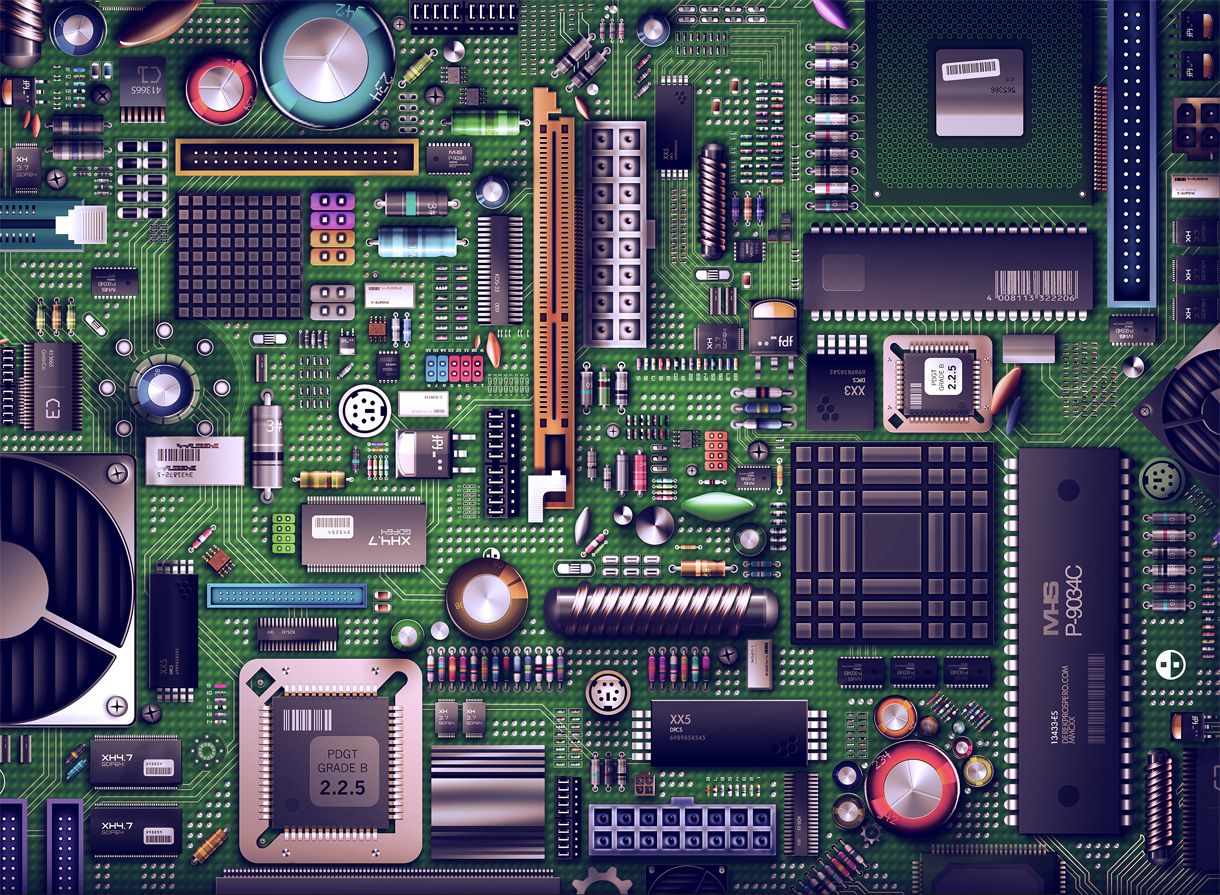
What does a motherboard do? The motherboard is a circuit board that includes different pathways for power and data to travel from one component to another. A motherboard also circulates power throughout the computer’s other components. These components are what make the computer work. Listed below are some of the ways that a motherboard functions. Read on to learn more. Also, consider the components of your computer, such as your processor, graphics card, and hard drive.
A motherboard has multiple slots for RAM, a single socket for the CPU, and a variety of other ports to connect peripherals such as video cards and sound cards. Each slot has a function, and motherboards typically have two to four memory slots. They also provide a connection point for various peripherals, including the network card, video card, and sound card. Lastly, the motherboard provides power to the power switch and loudspeaker cable.
The motherboard, also known as the main circuit board, is the main component of a PC. It serves as the central hub for all of the hardware in a PC, including the processor, video card, and memory. It also coordinates data flow between the hardware units. Moreover, it is necessary for a computer to function properly, because motherboards must be capable of managing temperature. As such, most motherboards have cooling fans attached, which protect the hardware and motherboard from overheating.
The northbridge is also known as the host bridge or the Memory Controller Hub. It is connected to the CPU via the front-side bus, and is responsible for all processes that demand maximum performance. The northbridge also manages communications with other components on the motherboard. BIOS, also known as system BIOS, PC BIOS, or ROM BIOS, is a program installed on the system board of the PC. It allows the computer to detect, diagnose, and resolve problems.
Another way the motherboard supports mass storage devices is by providing a front panel audio header. It also provides a connection for headphones and microphones. The audio header also acts as an interface for mass storage devices, such as a SATA hard drive, a CD-ROM, or an optical drive. Mass storage devices, like the SATA and PATA, are connected to the motherboard using the Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) protocol. Some motherboards also feature a floppy drive connection slot.
In short, the motherboard is a vital component of a computer system. It is the central communications hub, connecting all of the other components and external peripherals. There are different types of motherboards depending on speed, budget, and needs. You may want to consider the price of the board when purchasing a new one. You might want to choose the cheapest type available if you don’t need all of the bells and whistles of a high-end computer.
Motherboards also use VRM systems. These components provide the CPU with the exact amount of voltage it needs to run. They are easily recognizable as the flat rectangular components surrounding the CPU socket. Chokes are also included on a motherboard to stabilize currents and capacitors. The memory slots are located on the right-hand corner of the board and are used to house RAM modules. The number of memory slots depends on the model. You should choose a motherboard that has multiple chokes, which are connected to the CPU.