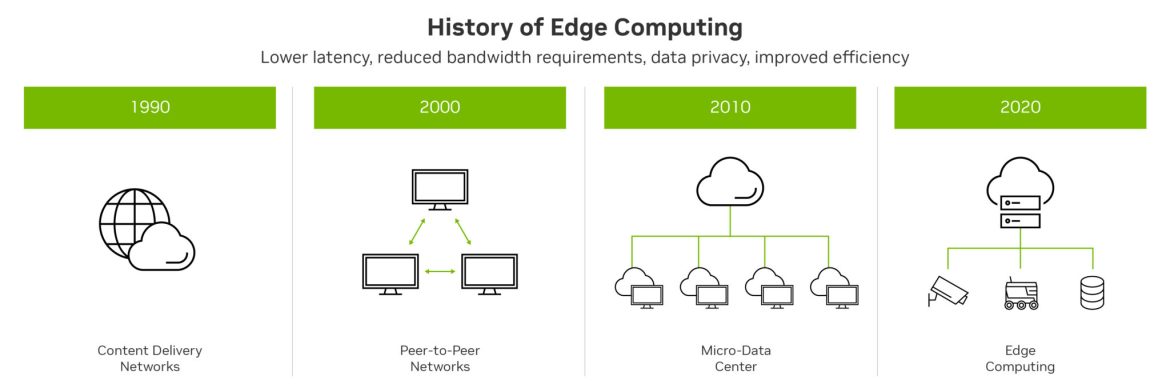
Ever clicked a link and waited… and waited… for the page to load? That’s latency—the annoying lag between your action and the internet’s response. For global users, high latency isn’t just frustrating; it’s a deal-breaker for real-time apps like gaming, video calls, or financial trading. Here’s where edge computing swoops in like a digital superhero.
What Is Edge Computing (And Why Should You Care)?
Edge computing processes data closer to where it’s generated—your phone, a factory sensor, a smart traffic light—instead of sending it to distant cloud servers. Think of it like neighborhood grocery stores versus a warehouse 100 miles away. Need milk? Grab it locally instead of waiting for a cross-country truck.
How Edge Computing Slashes Latency
Traditional cloud computing routes data through centralized servers, often continents away. Edge computing cuts the trip short:
- Distance matters: Data traveling fewer miles means faster response times. A gamer in Tokyo gets real-time feedback from a local edge node instead of a server in Texas.
- Bandwidth relief: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces congestion on overloaded networks—like adding express lanes to a highway.
- Real-time magic: Autonomous cars, AR/VR, and telemedicine rely on split-second decisions. Edge computing makes that possible.
Edge Computing in Action: Real-World Wins
Still abstract? Let’s look at tangible examples:
1. Gaming and Streaming
Cloud gaming services (think Xbox Cloud or NVIDIA GeForce Now) use edge servers to render games nearby. No more laggy sword fights or pixelated streams. Netflix? They cache popular shows on edge servers so your binge session doesn’t buffer.
2. Smart Cities
Traffic lights analyzing real-time data to ease congestion. Air quality sensors triggering instant alerts. Edge computing handles these locally, avoiding delays from distant data centers.
3. Healthcare
Remote surgeries need zero latency. Edge nodes process high-resolution video and robotic commands on-site—no room for lag when a scalpel’s involved.
The Global Impact: Bridging the Latency Gap
Not everyone lives next to a Google data center. Edge computing democratizes speed:
| Region | Average Latency (Cloud) | Average Latency (Edge) |
| North America | 45ms | 10ms |
| Europe | 60ms | 15ms |
| Southeast Asia | 120ms | 30ms |
For emerging markets, edge computing isn’t just nice—it’s essential. Mobile banking in Nairobi or e-learning in rural India can’t afford sluggish responses.
Challenges? Sure, It’s Not Perfect
Edge computing isn’t a silver bullet. A few hiccups:
- Cost: Deploying edge infrastructure globally isn’t cheap.
- Security: More nodes mean more attack surfaces—like securing hundreds of mini-fortresses instead of one castle.
- Standardization: Different vendors, different systems. Getting them to play nice takes work.
The Future: Edge Computing and 5G
5G and edge computing are peanut butter and jelly. 5G’s speed + edge’s proximity = near-instant connectivity. Imagine smart factories, holographic calls, or drone deliveries—all relying on this combo.
Honestly, we’re just scratching the surface. As IoT devices explode (projected to hit 29 billion by 2030), edge computing will shift from luxury to necessity.
Final Thought: Speed as a Human Right
In a world where milliseconds dictate stock trades, emergency responses, or even personal connections, latency isn’t just technical—it’s deeply human. Edge computing quietly bridges gaps, making the digital world feel a little more… instant.